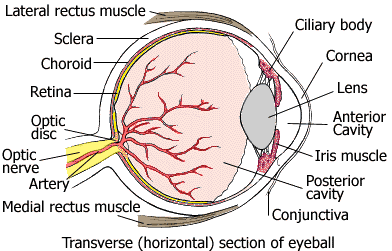
![]()
Vision is one of the most specialized of your 5 senses. The eyeball moves as a result of 6 muscles attached around it (2 of these muscles are illustrated below: the lateral rectus and medial rectus muscles).
The annotated structures of the eye are explained in the Table below the illustration.


![]()
| Anterior chamber | A cavity of the eye filled with aqueous humor, a fluid that provides oxygen, glucose, and proteins |
| Choroid | Layer rich in blood vessels that supply the eye tissues with oxygen and nutrients |
| Ciliary body | Changes the shape of the lens, which adjusts the eye's focus |
| Conjunctiva | Transparent membrane that covers the sclera and lines the insides of the eyelids |
| Cornea and lens | Focuses light |
| Fovea | A depression in the retina where cones (photoreceptor cells) are concentrated and vision is most acute. |
| Iris | Colored part of the eye |
| Optic disc | Round, flat structure where nerve fibers from the retina converge |
| Optic nerve | Transmits information about images to the brain |
| Retina | Contains light-sensitive nerve cells |
| Sclera | White, outer layer of the eyeball |
| Vitreous | Transparent gel that fills the main cavity of the eye |